
Photo Source: Unsplash
Single cell sequencing promotes the development of genomic medicine. This research report has extracted literature data from the Web of Science Core Database, and briefly analyzed the main papers in this field from 2016 to 2021 based on scientometric methodology.
1. Number of papers published
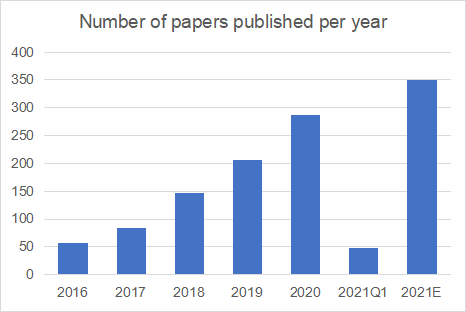
From 2016 to the first quarter of 2021, 832 major papers (excluding conference abstracts, reviews and works) related to single cell sequencing were published, and the number of published papers showed an upward trend. 58 papers were published in 2016, 288 in 2020 and 49 in the first quarter of 2021.
2. Citation of papers
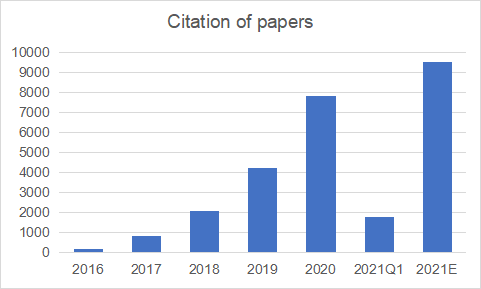
From 2016 to the first quarter of 2021, a total of 16, 903 papers (excluding conference abstracts, reviews and works) related to single cell sequencing were cited, and the citation rate showed an upward trend. The number of citations is 157 in 2016, 7, 809 in 2020 and 1, 781 in the first quarter of 2021.
3. Citation analysis
From 2016 to the first quarter of 2021, the 10 papers with the highest citation rate are shown in the table below. The research mainly involves oncology, immunology, single cell sequencing method improvement, spatial transcription analysis and bioinformatics.
|
Title |
Authors |
Publication name |
|
Landscape of Infiltrating T Cells in Liver Cancer Revealed by Single-Cell Sequencing |
Zheng, Chunhong, et al. |
CELL |
|
Comparative Analysis of Single-Cell RNA Sequencing Methods |
Ziegenhain, Christoph, et al. |
MOLECULAR CELL |
|
Single-Cell RNA Sequencing of Microglia throughout the Mouse Lifespan and in the Injured Brain Reveals Complex Cell-State Changes |
Hammond, Timothy R, et al. |
IMMUNITY |
|
Batch effects in single-cell RNA-sequencing data are corrected by matching mutual nearest neighbors |
Haghverdi, Laleh, et al. |
NATURE BIOTECHNOLOGY |
|
Pooling across cells to normalize single-cell RNA sequencing data with many zero counts |
Lun, Aaron T. L., et al. |
GENOME BIOLOGY |
|
Three-dimensional intact-tissue sequencing of single-cell transcriptional states |
Wang, Xiao, et al. |
SCIENCE |
|
Seq-Well: portable, low-cost RNA sequencing of single cells at high throughput |
Gierahn, Todd M., et al |
NATURE METHODS |
|
Parallel single-cell sequencing links transcriptional and epigenetic heterogeneity |
Angermueller, Christof, et al. |
NATURE METHODS |
|
Single-cell barcoding and sequencing using droplet microfluidics |
Zilionis, Rapolas, et al. |
NATURE PROTOCOLS |
|
The heterogeneity of human CD127(+) innate lymphoid cells revealed by single-cell RNA sequencing |
Bjorklund, Asa K., et al. |
NATURE IMMUNOLOGY |
4. Research field
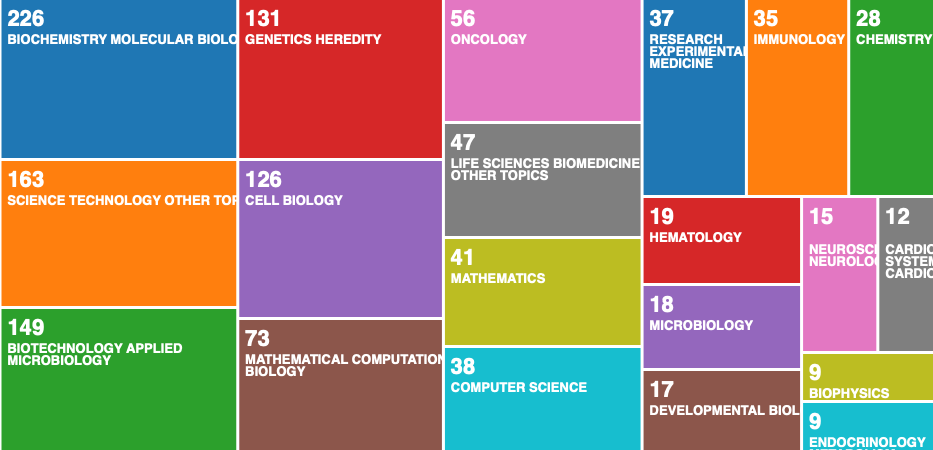
From 2016 to the first quarter of 2021, the research mainly involves biomedical engineering, biochemistry and molecular biology, genetics, cell biology, bioinformatics, oncology, microbiology and immunology, neurobiology, cardiovascular disease, endocrinology, mathematics and Computer Science (data from Web of Science).
5. countries and regions
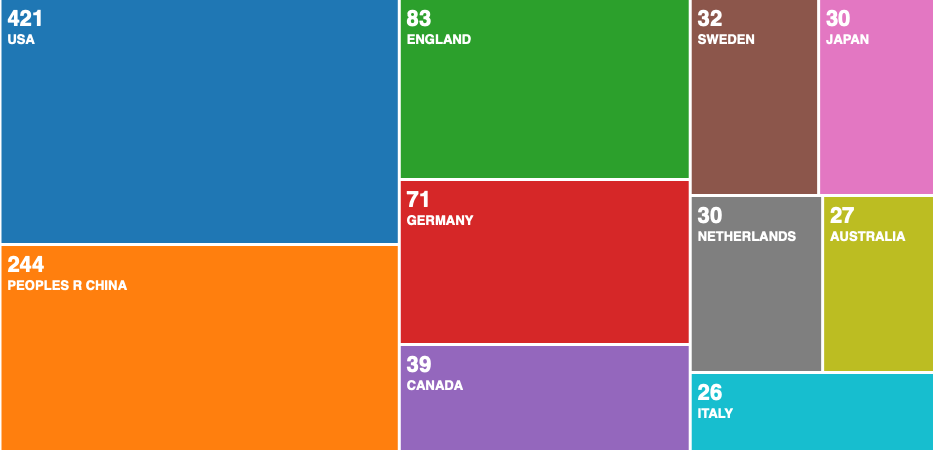
From 2016 to the first quarter of 2021, the research mainly came from the United States, China, the United Kingdom, Germany, Canada, Sweden, the Netherlands, Italy, Japan and Australia, etc.
6. Research institutions
From 2016 to the first quarter of 2021, the main research includes Peking University, Chinese Academy of Sciences system, Cambridge University, Stanford University, Harvard University system, etc.

7. Journal Publishing
From 2016 to the first quarter of 2021, the papers were mainly published in Nature Communication, Genome Biology, Science Report and other journals.
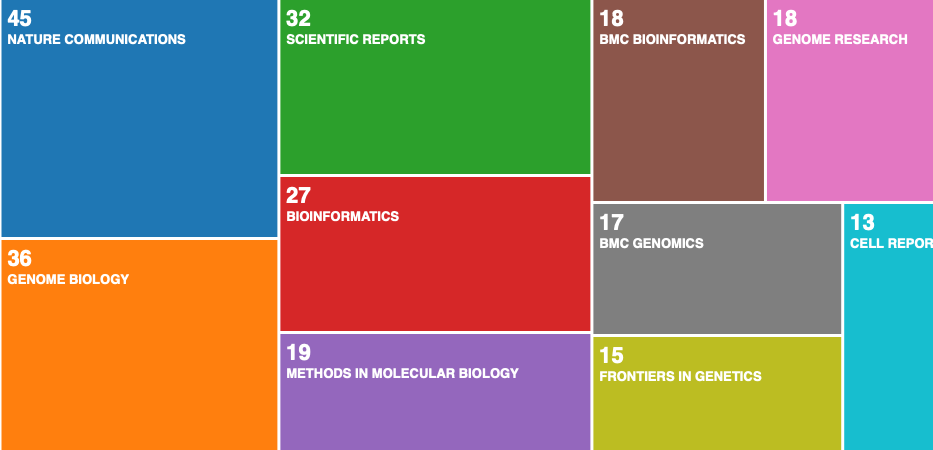
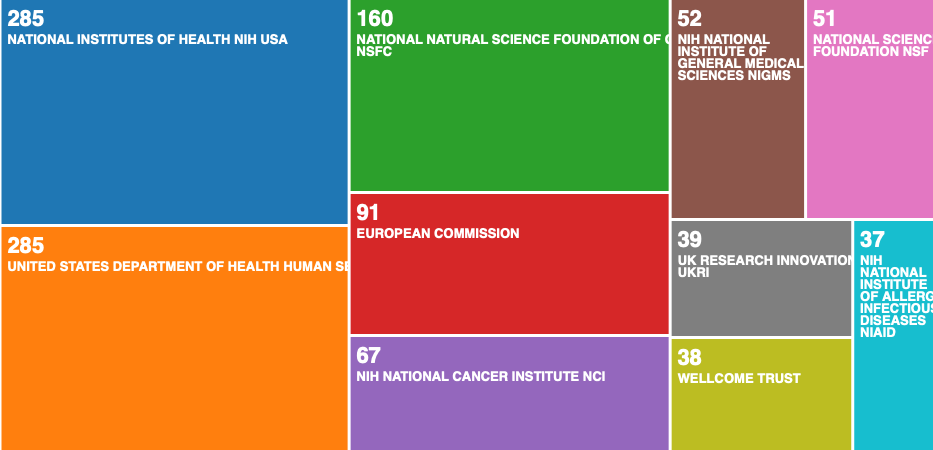
8. Fund supported institutions
From 2016 to the first quarter of 2021, the funds mainly came from NIH (285), HHS (285) and China National Nature Fund (160).
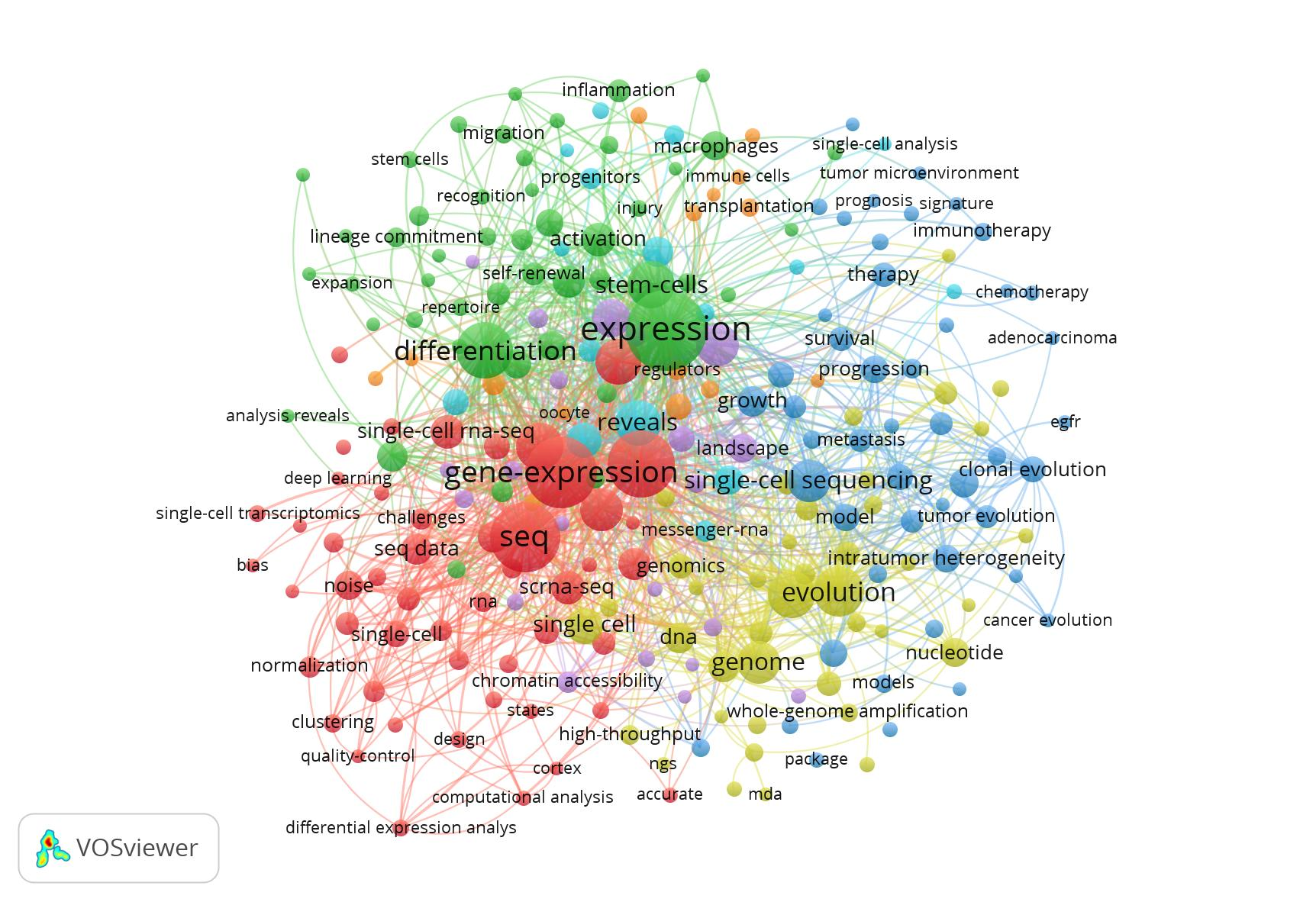
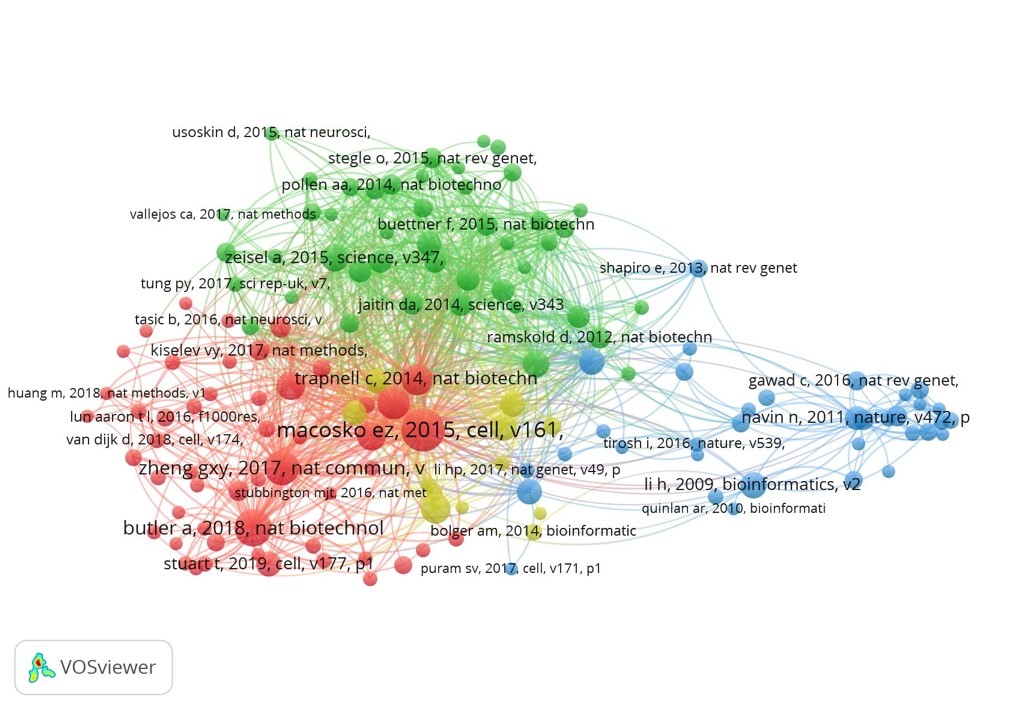
9. Co-occurrence analysis of research papers
We analyzes the correlation between keywords in the field of single-cell sequencing by using the common occurrence of keywords in the paper to describe the research direction and trend in this field (Vosviewer 1.6.15 was used in this analysis; The related methodology refers to the published literature of the software developer (Perianes-Rodriguez, A., Waltman, L., & Van Eck, N.J.. Constructing bibliometric networks: A comparison between full and fractional counting. Journal of Informetrics. 2016; 10: 1178-1195.). From 2016 to the first quarter of 2021, the main fields of single-cell sequencing are single-cell sequencing methodology and quality control (such as SMART Seq2), oncology (such as tumor microenvironment, circulating tumor cells and heterogeneity), stem cell (such as differentiation) and other fields (inflammation, islet cells, nerve cells and retina, etc.).
According to the published time axis, immune oncology and tumor microenvironment is one of the main direction of single cell sequencing research (yellow represents the new keywords of published papers).
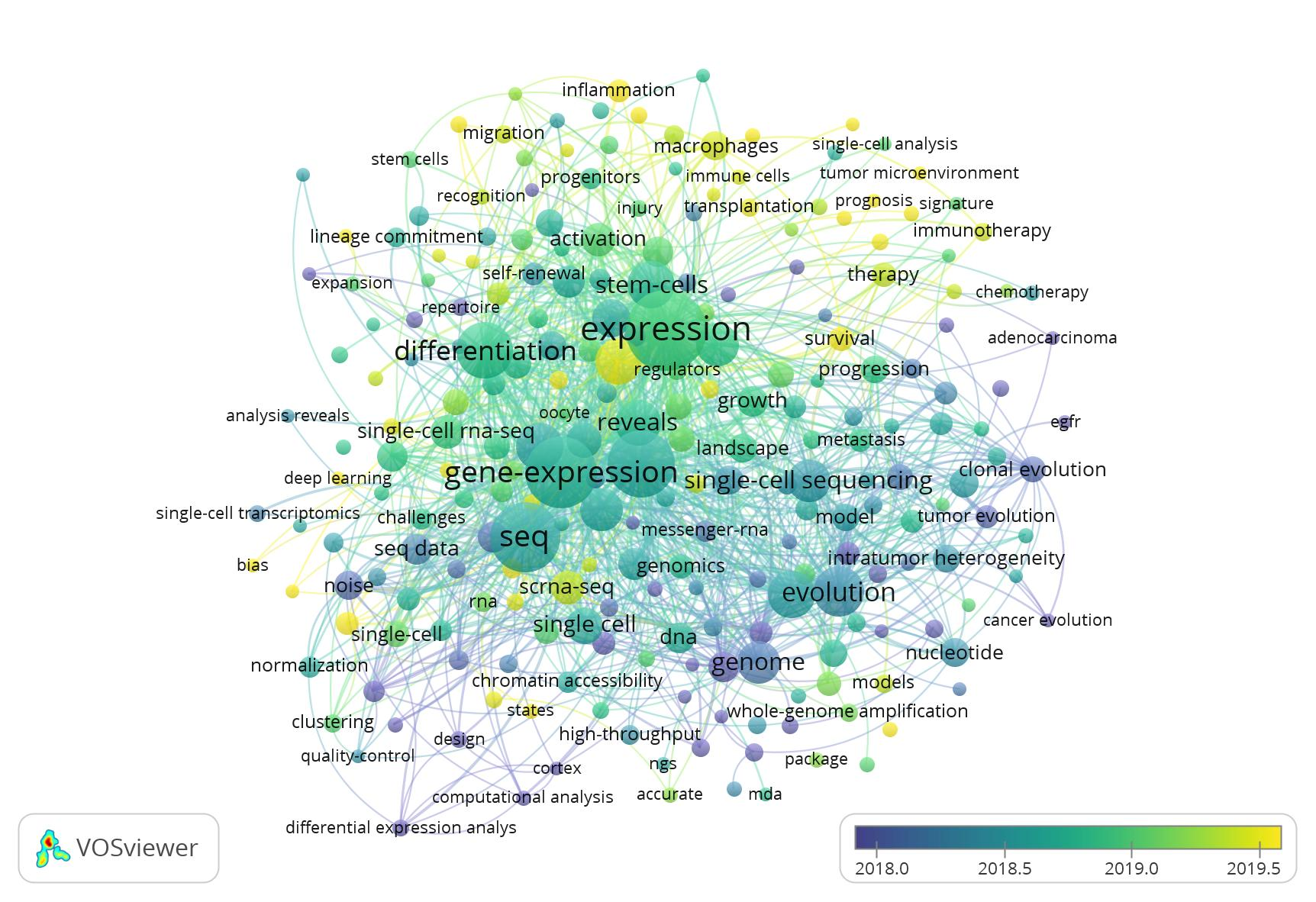
10. Co-citation of papers
Single cell sequencing system (such as DropSeq), bioinformatics methods and cancer research have formed three main types of citation.
Summary:
● Single cell sequencing has become a methodology and technology platform for the rapid development of genome research. The number of published papers is still small and in a period of rapid growth.
● Oncology, especially tumor microenvironment and immunotherapy of tumors (such as immune checkpoint, drug therapy evaluation, CAR-T, etc.) are paid more attention.
● Differentiation of stem cells, such as hematopoietic stem cells, is an important application scenario.
● China and the United States are in the leading position in this field. In China, Peking University, Chinese Academy of Sciences and Shanghai Jiaotong University have more research outputs.
● Single cell sequencing has obvious advantages in solving the differences between cells and cell differentiation. It may be necessary to increase the research on data processing, standardization of sequencing methods, reduction of systematic bias and clinical research.
● Whether single cell sequencing can be used in drug development, clinical diagnosis and treatment is worthy of attention.
CAVALIER PERSPECTIVE is a medical technology knowledge and opinion management organization. CAVALIER PERSPECTIVE mainly analyzes and shares medical technology knowledge and opinions, and helps scientists engaged in translational medicine research and entrepreneurs in biomedical companies to carry out knowledge innovation, technological innovation and product innovation. Currently, it is unable to provide consulting and business services for most organizations and customers. The website provides information for potential customers, such as researchers, scientists, students, business managers, and industry-related personnel. In any case, any information contained on this website shall not be sold for commercial purposes. This website does not contain any unauthorized data and patents of customers. Some research reports and data provided on this website may not be available to the public without authorization.
To view this content, in addition to using the CAVALIER PERSPECTIVE terms and privacy policy, you must agree to the following terms:
I confirm and agree to CAVALIER PERSPECTIVE:
By registering the following my information and clicking "Agree", I guarantee that I have read: